Reading Time: 6 minutes
Are you a homeowner tired of dealing with leaky pipes and constant plumbing repairs? Or perhaps you’re a plumber or architect seeking a reliable, cost-effective piping solution for your next project.
If so, then you’ve come to the right place! Today, we’ll delve into the world of uPVC pipes, a revolutionary material that’s changing the game in plumbing and construction. You may ask, what exactly are uPVC pipes, and what makes them such a popular choice for plumbing and other applications.
uPVC stands for unplasticized polyvinyl chloride. Unlike some other plastics, uPVC doesn’t contain plasticizers. This makes uPVC pipes incredibly strong, durable, and resistant to corrosion. These pipes are perfect for handling plumbing requirements in both residential and commercial properties.
So, whether you’re a homeowner curious about your plumbing system or a professional looking to expand your knowledge, keep reading to discover the many uses, features, and sizes of uPVC pipes!
Features of uPVC pipes
Imagine your home as a bustling city, with water flowing like traffic through an intricate network of pipes. But what makes these pipes reliable and long-lasting? The answer lies in the material itself – uPVC, or unplasticized polyvinyl chloride. uPVC pipes have become the go-to choice for plumbers and homeowners alike, and for good reason.
Let us look into the important features of uPVC pipes, uncovering why they are the best in the world of plumbing.
Durable and long lasting: uPVC’s rigid structure makes it highly resistant to cracks, impacts, and wear and tear. You can expect a long lifespan from uPVC piping systems.
Lightweight and easy to install: Compared to metal pipes, uPVC is significantly lighter, making transportation and installation a breeze.
Corrosion resistant: Unlike some metals, uPVC is not susceptible to rust or corrosion, ensuring long-term functionality even when exposed to moisture.
Chemical resistant: uPVC exhibits excellent resistance to a variety of chemicals commonly found in household and industrial applications.
Cost-effective: uPVC pipes offer a budget-friendly solution compared to many other pipe materials. They are relatively inexpensive to purchase and install.
Low maintenance: uPVC requires minimal maintenance thanks to its inherent durability and corrosion resistance.
Leak-proof: uPVC pipes form strong, secure joints, minimizing the risk of leaks and ensuring a reliable water flow.
Fire retardant: uPVC offers a degree of fire resistance, providing an added layer of safety in your home or building.
Versatile applications: uPVC pipes have a wide range of uses, from plumbing systems to electrical conduit and even drainage applications.
Eco-friendly: These pipes can be recycled at the end of its lifespan, making it a more environmentally friendly choice compared to some other pipe materials.
Uses/applications of uPVC pipes
uPVC pipes, known for their strength, affordability, and ease of use, have become a ubiquitous presence in various applications. Here are some of their prominent uses:
Potable water distribution: uPVC is a safe and reliable choice for transporting clean drinking water throughout homes and buildings.
Building applications: uPVC pipes can be used for rainwater harvesting systems, drainpipes, and even certain structural elements. Their durability and chemical resistance make them ideal for draining wastewater and sewage. uPVC pipes efficiently vent gases and Odors from plumbing systems.
Irrigation and agricultural systems: uPVC’s lightweight nature and affordability make it a popular choice for watering gardens and lawns. They can be used for greenhouse ventilation, hydroponic systems, and even livestock watering systems.
Underground conduit: uPVC pipes effectively protect electrical wires from damage and corrosion when buried underground.
Cable management: They organize and protect electrical cables within buildings, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Swimming pool systems: uPVC’s chemical resistance makes it suitable for pool filtration and circulation systems. For pressurized pipes Ashirvad Korrosafe is used
Industrial applications: uPVC pipes find use in various industrial settings for chemical transportation, dust collection, and other specific needs. Ashirvad Korrosafe is the choice for pipe and fittings both in the industrial applications.
This list highlights the versatility of uPVC pipes. Their ability to withstand various elements, chemicals, and pressures makes them a valuable material across numerous residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Available sizes of uPVC pipes
With so many sizes available of uPVC pipes, choosing the right one can feel like navigating a plumbing labyrinth. However, the size of the pipe depends on its application and there are various sizes of uPVC pipes based on their applications.
Potable water distribution: The size of the pipe is between 1/2” to 10” in diameter in Aqualife +. These sizes ensure a smooth flow for all your drinking, cooking, and cleaning needs.
Building applications: SWR pipes and Low Noise SWR pipes from Ashrivad’s size are according to IS standard type A and type B. Each type has its own designated sizing based on the specific water pressure and flow rate requirements of the building.
Irrigation and agricultural systems: Moving onto the agricultural systems, irrigation and sprinkler systems utilize pipes categorized under IS standard 4985. This standard classifies pipes based on pressure classes: Class 1, 2, and 3. The higher the class number, the greater the pressure the pipe can handle, ensuring efficient water delivery to your crops.
Underground conduit: For those burrowing beneath the surface, we need pipes that can handle the extra weight of the earth above. Here’s where IS 16098 Part 1 comes in. This standard specifies pipes with SN ratings – SN2, SN4, and SN8. These ratings indicate the pipe’s strength, with SN8 being the most robust option for withstanding significant underground pressure.
Swimming pool systems: Now, let’s take a dip into pool system piping. For maintaining a healthy flow of water throughout the pool, pipes typically range from ½ inch to a much larger 6 inches in diameter. The specific size depends on the size and complexity of the pool system.
Industrial applications: Finally, our industrial giants require pipes that can handle serious pressure. Here, we see a wider range of sizes, from a humble ½ inch all the way up to a whopping 12 inches. These pipes often come in Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 variations, which indicate wall thickness. Schedule 80 pipes have thicker walls for handling higher pressure applications within industrial settings.
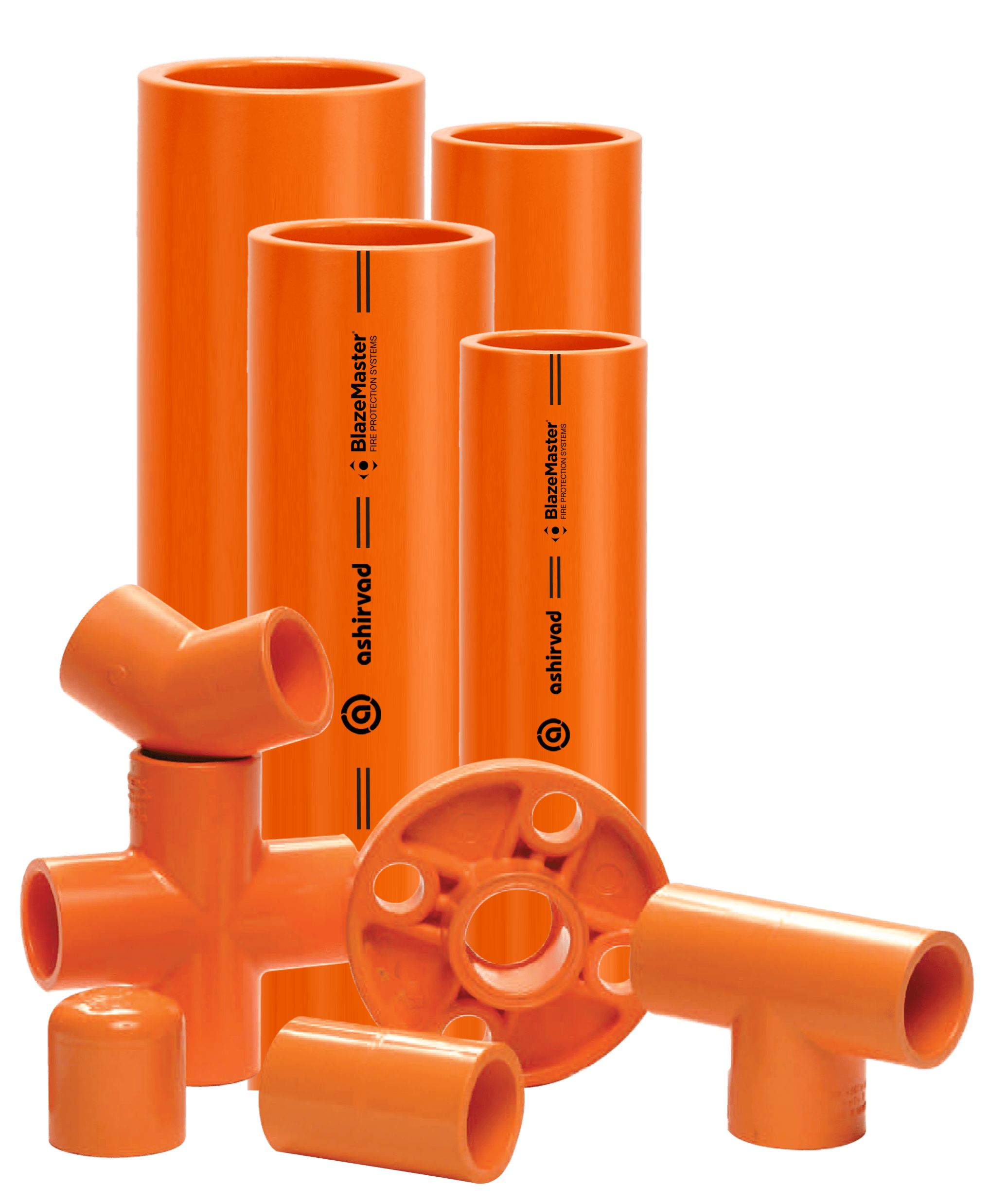
Fittings for uPVC pipes
Imagine a lot of straight pipes who can carry water and sewage from your home but are not able to twist or turn themselves when they have to. They will not be able to serve their purpose then.
So that is where the fittings for uPVC pipes come into the picture. These ingenious little gadgets, in all shapes and sizes, are the connectors, the adapters, the elbow benders, and the T-junction makers. They are the glue that holds the uPVC pipe world together, quite literally in some cases!
Imagine a brand-new house under construction. The shiny uPVC pipes are all lined up, eager to do their job. But how will the water from the main line get to the kitchen faucet? Enter the trusty coupler, a simple yet essential fitting that connects two pipes of the same size, creating a seamless flow.
Common types of fittings used with uPVC pipes:
- Couplings: Couplings are used to join two uPVC pipes together end-to-end. They are available in different sizes and can be either solvent cemented or threaded for connection.
- Elbows: Elbows are fittings that allow for changes in direction within a piping system. They come in 90-degree, 45-degree, and other angle configurations to redirect the flow of fluid.
- Tees: Tees are used to create branches in a piping system, allowing for the connection of a third pipe at a 90-degree angle to the main line.
- Reducers: Reducers are used to connect pipes of different diameters together. They can either reduce or increase the pipe size to accommodate changes in flow requirements.
- End cape: End caps are used to seal the end of a uPVC pipe. They are commonly used to cap off unused pipe ends or access points.
- Adapters: Adapters allow for the connection between uPVC pipes and pipes made from other materials such as metal or PVC.
- Ball valves: Ball valves are used to control the flow of fluid within a piping system. They have a ball with a hole in the middle that can be rotated to either allow or stop the flow of fluid.
- Check valves: Check valves (also known as non-return valves) allow fluid to flow in one direction only, preventing backflow.
- Sockets and caps: Sockets are used to connect pipes end-to-end using solvent cement, while caps are used to close off pipe ends permanently.
- Union fittings: Union fittings consist of two parts that can be easily disconnected for maintenance or repair purposes without cutting the pipe.
These fittings are typically made from uPVC material to ensure compatibility with uPVC pipes and resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation.
When selecting fittings for a uPVC piping system, it’s important to consider factors such as pipe diameter, pressure rating, and compatibility with the fluid being transported.
Additionally, fittings should be installed according to manufacturer guidelines and local plumbing codes to ensure a safe and leak-free system.
Conclusion
The uPVC pipe fittings are indispensable components in modern plumbing and fluid handling systems, offering a reliable and versatile solution for a wide range of applications.
Their unique combination of properties makes them a preferred choice across industries, emphasizing the significance of adopting uPVC technology for efficient infrastructure development and resource management.